
|
|
Canon 60D controls.
|
These settings are usually set with controls on the top or back of the camera and in the menus.
Program Mode - Set to Manual or Bulb.
Autofocus - Turn off, or set to Manual.
ISO - Set to 1600 for faint objects under dark skies. Set to a lower ISO for bright objects with a large dynamic range, or if shooting under a lot of light pollution.
Aperture - The aperture is fixed if you are shooting through a telescope so you can't change this.
For a camera lens:
Set to the widest aperture for a slow (f/2.8 to f/5.6) lens, or stop down one stop.
Stop down 2 - 3 stops for a fast (f/1.4 to f/2.8) lens. This will depend on the lens. Test to see what aperture produces acceptable stars.
Experiment to find the best compromise between light gathering at a wide, fast aperture, and better optical performance at a smaller, slower aperture.
Shutter Speed - Set to the correct exposure as determined by examining the histogram, which we will discuss in the next section. Up to 30 second exposures can be dialed in directly. For longer than 30 seconds, set to Bulb and control with a remote release timer. On some cameras, Bulb may be a separate exposure mode setting, or it may be accessed on the shutter speed dial one click past the 30-second setting.
White Balance - Set to daylight for an unmodified camera. For a modified camera, use a custom white balance set on a gray card in noon-sunshine on a clear day.
If you are using a light pollution filter, shoot the gray card with the filter on the camera.
Drive - Set to Single Shooting.
Color Space - Set to sRGB if shooting JPEGs in the camera. Doesn't matter if you are shooting Raw.
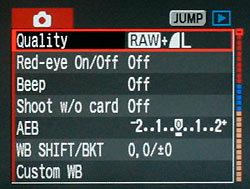
Quality: Raw vs JPEG - Set to Raw, or Raw + JPEG
|
|
Menu Settings
|
Most DSLR cameras come with the file format that images are stored in set to JPEG as the default. Most DSLR cameras also allow images to be saved in a proprietary "raw" file format that offers the potential for much higher image quality.
Raw file format preserves all of the original data as it comes from the sensor in the camera. This is, unquestionably, the best file format to use. The raw format saves the data in the high bit depth (12 or 14 bits) that comes out of the analog-digital converter as linear data. This is extremely important for astronomical images. High-bit linear data allows the most control over how the data is calibrated, manipulated and enhanced to produce the best images.
JPEG file format creates compressed files that take up less space on the memory card. JPEG images take the raw data produced by the sensor and processes it applying the white balance setting, a non-linear curve, and contrast, sharpening and saturation adjustments. A compression algorithm is then applied to the image which trades image data for storage space. This type of compression is called "lossy" because data is lost when it is discarded in the compression process. Raw files are "lossless" because all of the original data is present in them.
If you don't want to go to the trouble of shooting with raw files, and just want a quick image that you can show, you can certainly shoot JPEG-formatted files. The camera will turn the original linear file into a recognizable photograph, and you can touch it up later in an image editing program if you want to adjust the contrast and color balance. In fact, some new low-noise DSLR cameras as so good, that with brighter objects like M17, you can shoot a single 3 minute exposure in JPEG format and still get a good picture!
If you are a beginner, this may be the approach you want to take. Shoot JPEGs to get started and learn your way around the scope, camera, and astrophotography. Then as you advance to the next level of expertise, you'll want to start shooting raw file format.
Raw and JPEG Concurrently- Some cameras allow the user to shoot both raw and JPEG file formats concurrently in the camera, producing two files that are stored on the memory card. If you have a camera with this feature, you should try this. It does, however, take up more storage space on the memory card. The camera will apply whatever in-camera settings you have in terms of contrast and sharpening to the JPEG only, and it gives you a chance to take a quick peek at what the image looks like without having to process the raw file.
The in-camera settings for contrast, saturation, color balance and sharpening are not applied to the raw file, and the raw file preserves all of the original data as it comes from the sensor in the camera.
JPEG Compression - Set to the highest quality and lowest compression setting.
DSLR Cameras usually also offer different JPEG compression settings, sometimes also called "quality" settings. Higher quality means less compression which results in a larger file size. To fit more images on a card, for normal daytime snapshot photography, some people shoot with a lower quality setting that compresses the JPEG files more. Of course, you lose more information when you use higher-compression JPEG settings.
Raw Compression - Set to none, or turn off.
Some cameras offer an in-camera compression for their raw file formats that is different than the compression used with JPEG files. It may be lossy or lossless. This raw compression will be proprietary and you may only be able to access the file with the manufacturer's software. In general, I would advise against using raw compression. Memory storage is inexpensive enough to not have to use it.
Native Optical Resolution - Set to the highest optical resolution.
Many cameras offer different resolution settings. The camera's native optical resolution outputs the same number of pixels as the image is taken with. This is the setting you want to use. For example, the Canon 20Da offers a native optical resolution of 3504 x 2336 pixels, but also offers lower, interpolated resolutions of 2544 x 1696 pixels and 1728 x 1152 pixels.
You can always interpolate down to a smaller file size later in software, but if you do it in the camera to the original file, you can never get this lost data back.
Shutter Release Without Card - Set to Disable. This will prevent the camera from shooting without a memory card present.
Image Review - Turn off. The camera will display the image after the shutter closes. You can view an image after you shoot it by simply pressing the display button on the back of the camera. Having the image displayed after every shot will heat the camera up causing more thermal noise. It can also be very distracting to other people at a star party. After you have done your test exposures and focused and framed, you don't need to review every image if you are shooting a series of images for stacking.
Peripheral Illumination Correction - Set to Off. You can correct later during image processing.
Red-Eye Reduction - Set to disable. We won't use this for astrophotography.
Exposure Compensation / Auto Exposure Bracketing - Set to Zero. We won't use this for normal astrophotography because we are not using autoexposure.
Metering Mode - Set to Evaluative. This doesn't really matter as we won't use this for deep-sky. For lunar or solar work (with the proper safe solar filter), you can set it to spot metering.
White Balance Shift / Bracketing - Try adding some blue if you have set a custom white balance on the sky background.
Dust Delete Data - Set to none, or turn off. We won't use this for astrophotography.
ISO Auto - Set to default. We won't use this for astrophotography.
Canon Picture Styles and Nikon Picture Controls - Set to Standard or Neutral for Canon, and Standard or Vivid for Nikon.
Contrast - Increase for faint deep-sky objects. Turn down for star clusters.
Sharpening - Turn off for JPEGs shot in the camera. Sharpening can exaggerate any noise present in the image. Sharpening is not applied in the camera to raw images, but it is applied to JPEG images.
Saturation - Leave at default, or adjust to taste by shooting a test image.
Auto Power Off - Set to 1 minute.
Auto Rotate - Set to off.
Format - It is a good idea to format your memory card once in a while after you have copied your images to your computer. Warning! Formatting your memory card erases all images on it.
File Numbering - Set to Continuous.
LCD Auto Off - Set to disable.
Live View Function Settings - Enable Live View Shooting.
- Custom Functions
Exposure Level Increments - Set to 1/3 stop.
ISO Expansion - Set to off.
Long-Exposure Noise Reduction - If you are going to shoot just a couple of long-exposure frames in JPEG format at high ambient temperatures and don't plan to shoot separate darks, turn on in-camera long-exposure noise reduction.
If you are going to shoot multiple light frames for stacking and are shooting separate dark frames, then turn off long-exposure noise reduction.
This function is slightly misnamed as it does not really reduce "noise", but rather thermal signal, as we saw in the section on Sources of Signal in Chapter 3. You can usually access this setting through a custom function in the camera's menus.
In-camera noise reduction helps by reducing the thermal signal in the images. A few cameras have such low noise that it may not even be necessary to use long-exposure noise reduction (see M17). It depends on the length of the exposure, the ambient temperature, and the camera's ability to deal with thermal signal. Do a test and take two exposures at the length you plan to use, one with in-camera noise reduction on, and one with it off. Examine them and see how much of a difference it makes.
You should note that in-camera long-exposure noise reduction will essentially double the time it takes to take a picture. Say you want to take a one minute exposure of a subject. The shutter opens, and the one-minute exposure, called the "light frame" begins. It's called the "light frame" because photons of light are hitting the sensor in the camera and are being counted. This exposure ends, but the image is not immediately downloaded to the memory card in the camera. Instead, another exposure begins, of the same length as the light frame, but this time with the shutter closed. This exposure is called the "dark frame", because the camera is taking a picture of the dark, with no photons hitting the sensor from the subject. Instead it is taking a picture of the thermal signal in the camera. Because the thermal signal is consistent from frame to frame, if the frames are taken at the same temperature, the processor in the camera can then subtract the thermal signal in the dark frame from the light frame, thereby improving it.
Many people are often frustrated and confused when they take a long time-exposure with noise reduction turned on, and then it ends, but the busy light stays lit on the back of the camera for what seems like way too long. They think that surely it can't take that long for the image to be written to a card! It never takes that long during normal daytime photos. Well, that's right. It doesn't take that long for normal short exposures. The in-camera long-exposure noise reduction is only works for long exposures. It is taking that long because the camera is making a dark frame of the same length as the light frame and processing it in the camera before it is written to the memory card.
Once you get to a more advanced level in your astrophotography experience, you will definitely want to turn in-camera long-exposure noise reduction off. You will do better by shooting a series of dark-frame exposures yourself that you can use later in a more sophisticated way in calibrating the light-frame images later.
High ISO Speed Noise Reduction - Like long-exposure noise reduction, if you are going to shoot just a couple of long-exposure frames at a high ISO, turn on High ISO Speed Noise Reduction. If you are going to shoot multiple frames for stacking and are shooting separate dark frames, then turn it off.
Highlight Tone Priority - Set to disable.
Autofocus Assist Beam Firing - Set to disable.
Mirror Lock-Up - For long exposures with a very solid mounting, it probably is not necessary to lock the mirror up before an exposure. For short exposures for high-resolution planetary or double-star work, it is a good idea to lock the mirror up before the exposure to reduce camera movement and vibration caused by mirror slap. Some cameras access this setting with a control on top of the camera and some through a custom setting in a menu. Some cameras like the Canon 1000D (Digital Rebel XS) require the shutter to be pressed once to lock the mirror up, and then be pressed again to actually open the shutter. Take care to learn exactly how your camera works for this feature, because you could press the shutter thinking you have opened it for a long exposure and go off to do something else, and then come back only to find that all you had done was lock the mirror up and that no exposure had been taken. Some cameras do not offer a mirror lockup at all, but they may move the mirror up out of the way as the first thing when using the self timer. Read the camera manual to learn how your particular model works.
Shutter / AE Lock Button - Set to #1: AE Lock / AF. This transfers autofocus activation from the shutter release to the autoexposure lock button on the back of the camera.
LCD Display when Power On - Set to #1: Previous display status.
Add Image Verification Data - Set to disable.
Self Timer - If you don't have a remote release, you can use the camera's self-timer to trip the shutter so you don't have to touch the camera, which will help reduce vibrations and possible star trailing. Self-timer is usually set with the drive mode button on the back of the camera.
Built-in Flash - Turn off, because it won't reach to infinity. It won't even reach to the Moon.
Camera Settings for Astrophotography
- Program Mode - Set to Manual Exposure.
- Auto-focus - Turn off.
- White Balancee - Set to Daylight for a stock camera, set to Custom White balance set on a gray card in sunshine for a modified camera.
- Color Space - Set to sRGB, or Adobe RGB if extremely knowledgeable about color spaces.
- Drive - Set to Single Shot.
- ISO - Set to 1,600 for faint objects, set to ISO 400 for bright objects.
- Canon Picture Style / Nikon Picture Control - Set to Standard.
- Canon Auto Lighting Optimizer / Nikon Active-D Lighting - Turn off.
- Highlight Tone Priority - Turn off.
- Contrast - Increase for faint deep-sky objects. Turn down for star clusters.
- Sharpening - Set to low for long-exposure JPEG images.
- Saturation - Leave at default setting.
- Image Review - Turn off.
- Metering - Spot for solar and lunar.
- Exposure Compensation - Set to zero.
- Shutter Speed - Set to bulb for exposures longer than 30 seconds.
- Self Timer - Use if you don't have a remote release.
- Mirror Lock Up - Turn on for high resolution work.
- File Format - JPEG for Beginner's, and Raw (or Raw + JPEG) for more advanced users.
- JPEG Compression - Use the highest quality setting.
- Raw Compression - Turn off.
- Optical Resolution - Use the highest native optical resolution.
- Flash - Turn off.
- Red-Eye Reduction - Turn off.
- Long Exposure Noise Reduction - Turn on for single JPEGs. Turn off if you are shooting multiple darks.
- High-ISO Noise Reduction - Turn on for single JPEGs. Turn off if you are shooting multiple darks.
- Lens Peripheral Illumination Correction - Turn off.
|
|